Cryosphere: Earth’s Frozen Frontier and Climate Sentinel – Beneath the dazzling landscapes of snow and ice, the cryosphere stands as Earth’s frozen frontier—a realm of glaciers, ice sheets, frozen lakes, and frosty tundras. This icy expanse is not only captivating but also holds a critical role in shaping our planet’s climate and ecosystems.
This article embarks on a journey to unravel the essence of the cryosphere, its geographical presence, its significance, and the intriguing processes that give rise to its frozen beauty. idn slot
What is the Cryosphere?
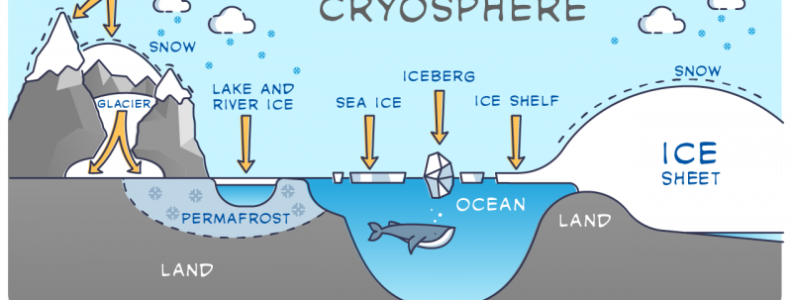
The cryosphere encompasses all the areas of the Earth’s surface where water exists in solid form, such as ice, snow, permafrost, and glaciers. This frozen realm extends across polar regions, mountain ranges, and even high-altitude landscapes. It is an integral part of the Earth system that profoundly influences global climate patterns, sea level dynamics, and ecological processes.

Where is the Cryosphere?
The cryosphere is found in regions where temperatures are consistently cold enough to sustain frozen water. This includes:
- Polar Ice Caps and Ice Sheets: The polar regions, particularly the Arctic and Antarctic, are home to vast expanses of ice sheets and sea ice.
- Glaciers and Mountain Ranges: Glaciers, which are large masses of ice that slowly flow under their own weight, can be found in mountainous areas around the world.
- Permafrost Zones: Permafrost, soil that remains frozen year-round, is prevalent in cold regions like the tundra.
- Frozen Lakes and Rivers: Lakes and rivers in cold climates can freeze over during the winter months, contributing to the cryosphere.
Why is the Cryosphere?
The cryosphere is of immense importance due to its multiple functions and impacts:
- Climate Regulation: Ice and snow reflect sunlight, helping to regulate Earth’s temperature and influence global climate patterns.
- Sea Level Dynamics: The melting of glaciers and ice sheets contributes to rising sea levels, impacting coastal regions and ecosystems.
- Ecosystem Support: The cryosphere supports unique ecosystems adapted to cold environments, such as polar bears in the Arctic and penguins in Antarctica.
- Freshwater Supply: Glacial meltwater feeds rivers and lakes, providing freshwater resources to communities downstream.
How is the Cryosphere Made?
The formation of the cryosphere is driven by processes of freezing and deposition:
- Snow Accumulation: Snowfall occurs when atmospheric moisture freezes in cold conditions, building up layers of snow on the ground.
- Glacier Formation: Over time, accumulated snow compresses under its own weight, transforming into ice and forming glaciers.
- Ice Sheets: Vast expanses of ice sheets result from the gradual accumulation of snow over thousands of years.
- Permafrost Formation: Permafrost forms when soil temperatures remain below freezing for extended periods, causing water in the soil to freeze.
Conclusion: Guardians of Frozen Beauty
The cryosphere, with its shimmering glaciers, frozen lakes, and majestic ice sheets, embodies the delicate balance between Earth’s dynamic systems. As we gaze upon this frozen landscape, we witness the power of nature to create and shape our world.
Beyond its captivating beauty, the cryosphere plays a crucial role in maintaining our planet’s climate equilibrium and supporting a diverse range of ecosystems. As we continue to explore and understand the cryosphere’s intricate interactions, we gain insights into the interwoven tapestry of Earth’s processes and the significance of its frozen splendor.